reading_notes
Read: 09 - Forms and Events:
Forms:
An HTML form is used to collect user input. The user input is most often sent to a server for processing.
Types of Form Controls:
How Forms Work?
- A user fills in a form and then presses a button to submit the information to the server.
- The name of each form control is sent to the server along with the value the user enters or selects.
- The server processes the information using a programming language It may also store it in a database.
- The server creates a new page to send back to the browser based on the information received.
Form Structure:
<form action="http://www.example.com/subscribe.php" method="get">
<form> controls live inside a <form> element.
<action> Its value is the URL for the page on the server that will receive the
information in the form when it is submitted.
<method> Forms can be sent using one of two methods: <get> or <post>
<get>: the values from the form are added to the end of the URL
ideal when: short forms or just retrieving data from the web server (not sending)
<post>: values are sent in what are known as HTTP headers.
ideal when the form: upload a file, very long, contains sensitive data, add or delete from database.
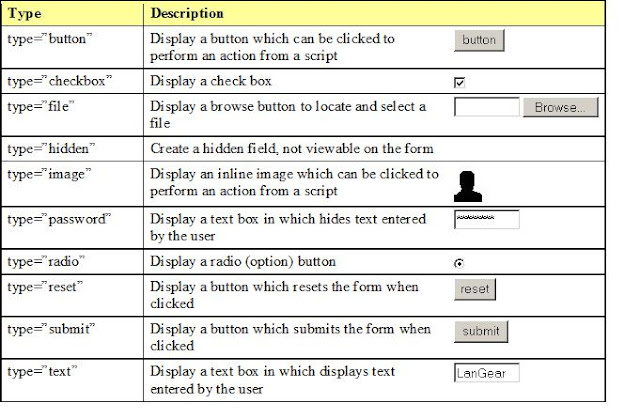
- form consists of: input or textarea, type, name, value, and you can add size or maxlength
- types: “text”, “password”, “radio”, “checkbox”, “file”, “submit”, “image”, “hidden”
- “
<button>you can combine text and images between these tags</button><label>indicating the purpose of each one in text next to it.<fieldset>You can group related form controls together inside the<fieldset>element.<legend>come after<fieldset>and contains a caption, identify the purpose of group of form controls.
HTML5 Form Validation:
- Forms on the web that give users messages if the form control has not been filled in correctly.
- Validation helps ensure the user enters information in a form that the server will be able to understand when the form is submitted.
- Date input:
<input type="date" />, Email & URL Input:<input type="email" />,<input type="url" /> - Search Input:
<input type="search" name="search" placeholder="Enter keyword" /> <input type="submit" />
Lists, Tables & Forms:
Bullet Point Styles:
list-style-type:
Property allows you to control the shape or style of a bullet point (also known as a marker).
- For an unordered list you can use the following values: none, disc, circle, square.
- For an ordered list: decimal, decimal-leading-zero, lower-alpha, upper-alpha, lower-roman, upper-roman.
list-style-image:
You can specify an image to act as a bullet point using the list-style-image property.
- The value starts with the letters url and is followed by link of image in “ “ inside a pair of parentheses.
list-style-position:
Indicates whether the marker should appear on the inside or the outside of the box containing the main points.
outside: list-style-position: outside; , inside: list-style-position: inside;
list-style:
Shorthand allows you to express the markers’ style, image and position properties in any order.
Table Properties:
- width to set the width of the table
- padding to set the space between the border of each table cell and its content
- text-transform to convert the content of the table headers to uppercase,lowercase or anothers…
- letter-spacing, font-size to add additional styling to the content of the table headers
- border-top, border-bottom to set borders above and below the table headers
- text-align to align the writing to the left of some table cells and to the right of the others
- background-color to change the background color of the table rows
- :hover to highlight a table row when a user’s mouse goes over it
Border on Empty Cells:
To specify whether or not their borders should be shown; If you have empty cells inyour table.
empty-cells: show;This shows the borders of any empty cells.empty-cells: hide;This hides the borders of any empty cells.empty-cells: inherit;This instructs the table cells to obey the rules of the containing table.
Gaps Between Cells:
- The border-spacing property allows you to control the distance between adjacent cells.
- The border-collapse property: border-spacing will be ignored and cells pushed together, and empty-cells properties will be ignored.
- border-separate: Borders are detached from each other. (border-spacing and empty-cells will be obeyed.)
Styling Forms:
Styling Text Inputs:
- font-size sets the size of the text entered by the user.
- color sets the text color, and background-color sets the background color of the input.
- border adds a border around the edge of the input box
- border-radius can be used to create rounded corners.
- The :focus pseudo-class is used to change the background color of the text input
- The :hover psuedo-class applies the same styles when the user hovers over them.
- background-image adds a background image to the box.
Styling Submit Buttons:
- color is used to change the color of the text on the button.
- text-shadow can give a 3D look to the text in browsers that support this property.
- border-bottom has been used to make the bottom border of the button slightly thicker
- background-color can make the submit button stand out from other items around it.
- The :hover pseudo-class change the appearance of the button when the user hovers over it.
Styling Fieldsets & Legends:
- width is used to control the width of the fieldset
- color is used to control the color of text.
- background-color is used to change the color behind these items.
- border is used to control the appearance of the border around the fieldset and/or legend.
- border-radius is used to soften the edges of these elements in browsers that support this property.
- padding can be used to add space inside these elements.
Aligning Form Controls: Problem:
Labels for form elements are often different lengths, so the form controls will not appear in a straight line.
The solution: each topic we ask the user about is placed inside a <div> element to ensure that each question appears on a new line. Then we use styling by css and easily select forms by div and span.
Cursor Styles:
The cursor property allows you to control the type of mouse cursor that should be displayed to users. Types: auto, crosshair, default, pointer, move, text, wait, help, url(“ “)
Events:
HTML events are “things” that happen to HTML elements.
When JavaScript is used in HTML pages, JavaScript can “react” on these events.
examples of HTML events:
- An HTML web page has finished loading
- An HTML input field was changed
- An HTML button was clicked
Common HTML Events
| Event | Description | |———|————| | onchange | An HTML element has been changed | | onclick | The user clicks an HTML element | | onmouseover | The user moves the mouse over an HTML element | | onmouseout | The user moves the mouse away from an HTML element | | onkeydown | The user pushes a keyboard key | | onload | The browser has finished loading the page |
TERMINOLOGY
- When an event has occurred, it is often described as having fired or been raised
- Events are said to t rigger a function or script. When the click event fires on the element.
| Event | Description |
|---|---|
| input | Value in any <input> or <textarea> element has changed |
| change | Value in select box, checkbox, or radio button changes |
| submit | User submits a form (using a button or a key) |
| cut | User cuts content from a form field |
| copy | User copies content from a form field |
| Paste | User pastes content into a form field |
| select | User selects some text in a form field |
How Events Trigger JavaScript Code:
event handling:
- Select the element node(s) you want the script to respond to.
- Indicate which event on the selected node(s) will trigger the response.
- State the code you want to run when the event occurs.

Three ways to bind an event to an element:
1- HTML Event Handlers 2- Traditional DOM Event Handlers 3- DOM Level 2 Event Listeners
Traditional DOM Event Handlers:

Event Listeners:

Simple Summary from the book:
- Events are the browser’s way of indicating when something has happened (such as when a page has finished loading or a button has been clicked).
- Binding is the process of stating which event you are waiting to happen, and which element you are waiting for that event to happen upon.
- When an event occurs on an element, it can trigger a JavaScript function. When this function then changes the web page in some way, it feels interactive because it has responded to the user.
- You can use event delegation to monitor for events that happen on all of the children of an element.
- The most commonly used events are W3C DOM events, although there are others in the HTMLS specification as well as browser-specific events.