reading_notes
Intro to Serverless
Serverless is a cloud computing execution model where the cloud provider dynamically manages the allocation and provisioning of servers. A serverless application runs in stateless compute containers that are event-triggered, ephemeral (may last for one invocation), and fully managed by the cloud provider.
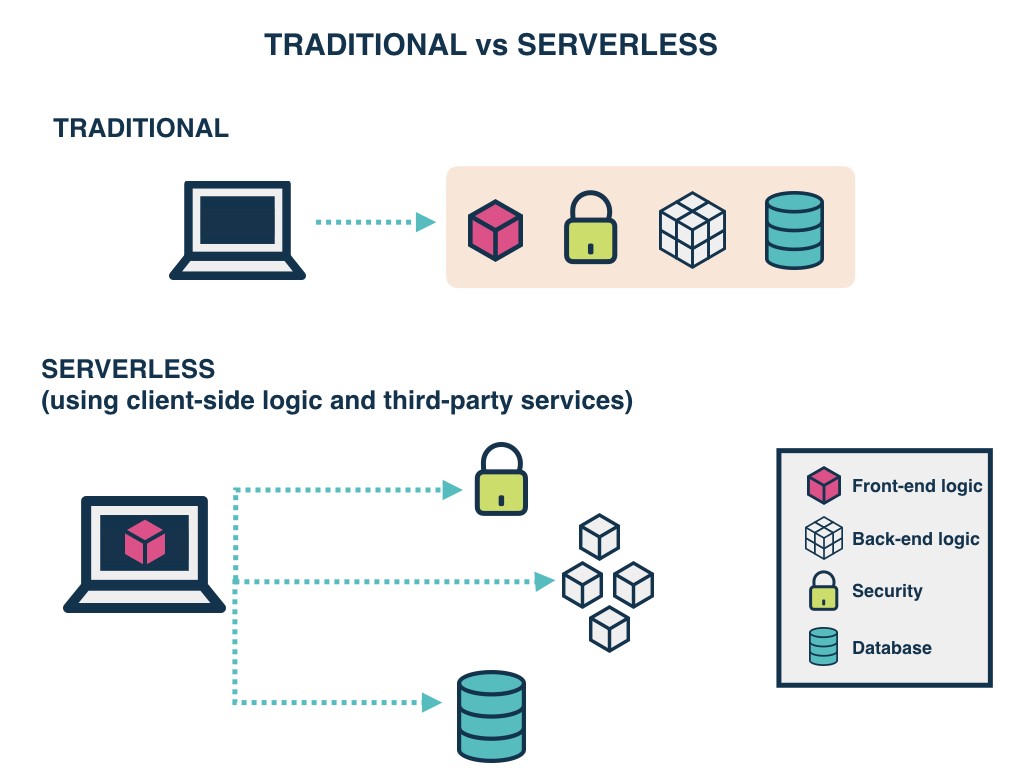
Serverless applications are event-driven cloud-based systems where application development rely solely on a combination of third-party services, client-side logic and cloud-hosted remote procedure calls (Functions as a Service).
- Example of Cloud Services:
- Traditional VS. Serverless
Pricing
One of the major advantages of using Serverless is reduced cost, for years the cost of provisioning servers and maintaining that 24x7 server team which blew a hole in your pocket is gone. The cost model of Serverless is execution-based: you’re charged for the number of executions.
Networking
The downside is that Serverless functions are accessed only as private APIs. To access these you must set up an API Gateway.
3rd Party Dependencies
Most, if not all of your projects have external dependencies, they rely on libraries that are not built into the language or framework you use. You often use libraries with functionality that includes cryptography, image processing, etc., these libraries can be pretty heavy. Without system-level access, you must package these dependencies into the application itself.
Environments
Timeout With Serverless computing, there’s a hard 300-second timeout limit. Too complex or long-running functions aren’t good for Serverless, but having a hard timeout makes it impossible to perform certain tasks.
Scale
Principles of FaaS: 1- Complete management of servers
2- Invocation based billing
3- Event-driven and instantaneously scalable
Key properties of FaaS:
Independent, server-side, logical functions
The Serverless App
A Serverless solution consists of a web server, Lambda functions (FaaS), security token service (STS), user authentication and database.
Client Application => The UI of your application is rendered client side in Modern Frontend Javascript App which allows us to use a simple, static web server.
Web Server => Amazon S3 provides a robust and simple web server. All of the static HTML, CSS and JS files for our application can be served from S3.
Lambda functions (FaaS)
They are the key enablers in Serverless architecture. Some popular examples of FaaS are AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions and Microsoft Azure Functions. AWS Lambda is used in this framework. The application services for logging in and accessing data will be built as Lambda functions. These functions will read and write from your database and provide JSON responses.
Security Token Service (STS)
generates temporary AWS credentials (API key and secret key) for users of the application. These temporary credentials are used by the client application to invoke the AWS API (and thus invoke Lambda).
User Authentication
AWS Cognito is an identity service which is integrated with AWS Lambda. With Amazon Cognito, you can easily add user sign-up and sign-in to your mobile and web apps. It also has the options to authenticate users through social identity providers such as Facebook, Twitter or Amazon, with SAML identity solutions, or using your own identity system.
Database
AWS DynamoDB provides a fully managed NoSQL database. DynamoDB is not essential for a serverless application but is used as an example here.
AWS Amplify
AWS Amplify is a set of purpose-built tools and services that makes it quick and easy for front-end web and mobile developers build full-stack applications on AWS, with the flexibility to leverage the breadth of AWS services to further customize applications. Amplify supports popular languages, frameworks, and platforms, including JavaScript, React, Angular, Vue, and Next.js for web apps and Android, iOS, React Native, Ionic, and Flutter for mobile apps.
.86135eef1e1961cf5cc41fba8c1a5fc46bf38cf2.png)
GraphQL
“The GraphQL Transform provides a simple to use abstraction that helps you quickly create backend for your web and mobile applications on AWS. With the GraphQL Transform, you define your application’s data model using the GraphQL Schema Definition Language (SDL) and the library handles converting your SDL definition into a set of fully descriptive AWS CloudFormation templates that implement your data model.”
- Works in conjunction with AWS Amplify to quickly create backend.
- Assets in building a data model you use for your app
“The GraphQL Transform simplifies the process of developing, deploying, and maintaining GraphQL APIs. With it, you define your API using the GraphQL Schema Definition Language (SDL) and can then use automation to transform it into a fully descriptive cloudformation template that implements the spec. The transform also provides a framework through which you can define your own transformers as @directives for custom workflows.”
